Recent

Long before Owen J. Morgan founded the Global Ecology Group, he dedicated his time to the study and development of biocompatible decontamination and remediation technologies. This goes back to the 1990s, and it was all triggered by a visit to the zoo.
It is a well-known fact that animals living within water enclosures are regularly bombarded with disinfecting agents, to ward off contaminations and diseases. “On a visit to the zoo, I noticed that the sea lions were suffering from cataract,” says Owen.
He asked the zookeeper for an explanation, who “was sure that it is the chlorine they use to keep the water clean that causes the problem. I found this unacceptable. The sea lions were suffering. We knew why. And yet there was no alternative available to keep the enclosure clean,” Owen remembers.
Fuelled by this frustration, Owen embarked on seeking an alternative. The aim was to find a non-chlorine and non-ozone based water sanitisation solution while being at least equally effective, safe to animals, humans and the environment, with none of the adverse effects of chlorine or ozone.
Owen’s research branched in several directions. “One of them was focusing on understanding the impact of electrical charge, frequency and light on living organisms,” he explains. Through this research, Owen came across the scientific principles of electro-chemically activated solutions (ECAS).
Through the application of electrical current to saline water, it becomes electrochemically activated. It is in a metastable state. Characterised by exceptional antimicrobial activity – based on the interaction of the oxidative ions, the high redox potential (> 1,100 mV) and the low pH – ECAS are superior to common chemical disinfectants.
“Advanced ECAS are effective against a wide range of pathogens upon contact – removing viruses, bacteria, germs, fungi and their spores. It is an environmentally friendly, fast-acting disinfectant solution with no petrochemical ingredients,” says Owen.
In Russia, ECAS were used for the treatment of drinking water in their national space programme and hospitals for disinfecting purposes since the 1970s. In the 1980s, ECAS became popular in Japan as well, used to sterilise medical instruments, followed by applications in the cultivation of plants and livestock farming.
#Explained 1|4 with Prof. @Reynolds_UWE, @UWEBristol
Interested in the #Science behind #ECAS | #ESOL? Let’s look at the historic development and use of Electro-Chemically Activated Solutions (ECAS) first. https://t.co/sKpbBAR9j0— Global Ecology Group (@gegecology) June 30, 2020
After some time has passed, the so-called relaxation time, ECAS reacts back into its original state. Thus, only water and salts remain. “The ECAS principle seemed feasible for the problem of the sea lions in the zoo, and I founded Pure Water Science and developed a ‘free radical’ generation chamber for commercial applications in the United Kingdom,” says Owen.
Since then, Owen has been fully committed to researching and developing a wide range of eco-technologies – alternative environmentally friendly solutions for water, soil, air and waste remediation. Owen’s know-how has been instrumental in meeting real-world disasters with ethically responsible countermeasures.
Up to now, Owen promotes and furthers the use of affordable and versatile ECAS. Amidst the global COVID-19 pandemic, he developed and advanced an ECAS fogging system, keeping surfaces in our homes, offices, hospitals, stores and vehicles safe at all times, with no adverse effects on humans or the environment.
Meanwhile, the ECAS technology has also evolved. With new high-performance materials for electrolysis systems, the industrial application of ECAS has become more established as an eco-friendly and user-friendly technology in many different fields all over the world.
And the sea lions? They can attest to the positive effects of ECAS: systems installed in water parks and zoological centres prove to be highly effective at replacing chlorine dose systems in zoological water enclosures and significantly reducing the occurrence of cataracts in sea lions and penguins.
WHAT WE FIND INTERESTING:
→ To maintain best practice animal husbandry and staff and visitor hygiene, Zoos Victoria rely on a range of chemicals for cleaning, sanitising and disinfecting. For better environmental outcomes, Zoos Victoria plans to reduce their dependence on chemicals by using electrolysed water [page 43].
We live in a time when each of our actions should be the result of an internal negotiation, making a cost-benefit analysis for each of our steps. We must, however, be entirely aware that we, alone, are not the ones to pay the price, rather our planet and future generations.
In just over four decades, wildlife populations around the world have decreased by 60 percent, according to the World Wildlife Fund’s (WFF) Living Planet Report. More than 4,000 mammal, bird, fish, reptile and amphibian species have shrunk dramatically between 1970 and 2014.
And if business as usual continues, the global demand for water will exceed viable resources by 40 percent by 2030. “Water is something that we should all be focusing on. As a resource, we should really make sure we keep it, as much as we can,” says the Global Ecology Group (GEG) Founder and CEO Owen J. Morgan.
We also “have damaged the soil matrix”, adds Owen. By now, a third of the planet’s land is severely degraded, and fertile soil is being lost at the rate of 24 billion tonnes a year, according to the United Nations.
Ninety-three percent of children worldwide inhale poisoned air. Experts estimate that 600,000 children died in 2016 as a result of air pollution.
Pollution, deforestation, climate change and other human-made factors have led to a severe crisis. And yet, the younger generations have been for long excluded from the conversations about conservation.
WHAT WE FIND INTERESTING:
→ The Fridays For Future “Declaration of Lausanne” | August 2019, by 400 climate activists from 38 countries.
But, in recent years, this has changed. Young environmental activists like Greta Thunberg have gained international recognition for promoting the view that humanity is facing an existential crisis arising from climate change.
In August 2018, the by then 15-year-old Greta and other young activists sat in front of the Swedish parliament every school-day for three weeks, to protest against the lack of action on the climate crisis.
She posted what she was doing on Instagram and Twitter, and it soon went viral, inspiring the global #FridaysForFuture movement. “Kids have a voice now, and they have a voice on a global scale. Because they can network at a level that we have never been able to,” says Owen.
Within the debate of equitable sharing of responsibilities, it is essential to include the younger generations. It is also crucial to build upon global and multigenerational collaboration to start addressing climate change and environmental degradation.
We are meeting unprecedented challenges, and “I really believe that it is the time for us to actually listen to the next generations”, says Owen. It is upon all of us to give their ideas and visions the required space to flourish and spark the difference.
Air pollution is a severe concern in many parts of the world, and the COVID-19 pandemic highlighted just how human actions truly impact air quality.
The global coronavirus pandemic is having a devastating effect on economies worldwide. However, one of the few positive consequences of travel restrictions and the industry downturn has been a temporary reduction in air pollution. This has made skies cleaner and clearer.
Both of Africa’s tallest peaks, Mt. Kilimanjaro and Mt. Kenya clearly visible from Nairobi this morning at almost 180° apart. Photos by @marquington pic.twitter.com/ssfVa257Kn
— Kenya Pics (@kenyapics) April 16, 2020
In places like China, for instance, satellites captured the sharp drop in air pollution amid the pandemic lockdowns, but levels quickly bounced back once the restrictions were eased.
Urban residents across Europe do not want to see air pollution return to pre-COVID-19 levels. They support profound changes to protect clean air, according to fresh YouGov opinion polling in 21 European cities.
“Air is the one thing we can’t live without,” says Owen J. Morgan, Global Ecology Group Founder and CEO. Yet, the air we breath is one manifestation of our poisonous ambition. “We have damaged air so much,” Owen adds.
“There is currently a PhD student in London who is monitoring the air over the university where they are, and there are nanoparticles of plastic in every sample they are taking,” says Owen. “It’s insane.”
And indeed, particulate matter, nitrogen dioxide, ground-level ozone – more than 90 percent of children worldwide inhale poisoned air. Dirty air is the “new tobacco”, the Guardian quotes the World Health Organisation Director Tedros Adhanom.
WHAT WE FIND INTERESTING:
→ Now, anyone can monitor the nitrogen dioxide concentrations at any place from anywhere in the world using the ESA’s new online platform that allows people to track air pollution, whether on a global scale or for their particular regions or cities.
Experts estimate that 600,000 children died in 2016 as a result of air pollution. 1.8 billion children are exposed to air that is so polluted that it seriously jeopardises their health and development.
Air pollution is the most significant environmental health risk in Europe, according to the European Environment Agency. It caused about 400,000 premature deaths in the EU in 2016, the EU agency estimates. And those living in polluted, big cities are more at risk from COVID-19, EPHA has warned.
Yet only 13 percent of Brits believe air pollution to be “a very big problem”, according to a YouGov poll.
As levels of air pollution plummeted when countries imposed pandemic lockdown measures, it is evident that it is in our hands to improve the air we breathe. With combined efforts, like those proposed in the European Green Deal initiative, we can make a change.
“We really need to make sure that the air we are breathing is good. Water – doable; soils – doable; air – not so much. I really don’t know how we fix air. Maybe we can’t. Maybe we have to learn to live with the air that we’ve got. But let’s not do more to it than we have already done.”
GEG’s ethos is respecting the sanctity of the natural world and our place in it. Through innovations like Ennea, the Harvester and ESOL™ solutions, GEG’s Research and Development paves the way towards improving current industry practices by meeting complex environmental challenges like air pollution.
P.S.: Owen’s got one more suggestion…
Together we can act #ForNature
One easy way → take your bicycle more often and ride for nature… #Nature #NatureNow #NatureLove #GEG #BicycleWaltz #WorldEnvironmentDay https://t.co/NwLry1XVse— Global Ecology Group (@gegecology) June 5, 2020
It is sad and ironic that one of the most fundamental pillars of our existence, food, is threatening the one single element which makes feeding almost 8 billion of us possible – soil.
Agriculture has been a foundational component of our evolution as a species. The agricultural revolution over 10,000 years ago led to settlements, which in turn led to cities, contact diseases, architecture, trade centres, currency, technology and the modern human.
We owe much of our daily comforts and existential questions to agriculture. Our diets changed, and so did our lifestyles and our understanding and our moulding of the world.
Today we face questions that should have been answered long ago: How healthy is the food we consume? How does climate change affect the quality of our produce? And to what extent shall we sacrifice our personal comfort for the good, and most probably the survival of the next generations of our species?
To start answering these questions, we must be aware that one element upon which our whole agricultural system relies is now at risk. “We have damaged the soil matrix,” says Owen J. Morgan, Global Ecology Group Founder and CEO.
In addition to erosion, soil quality is affected by other aspects of agriculture. These impacts include compaction, loss of soil structure, nutrient degradation, and soil salinity.
By now, a third of the planet’s land is severely degraded, and fertile soil is being lost at the rate of 24 billion tonnes a year, according to the United Nations.
Whether it is pesticides, mono-cropping or synthetic fertilisers, the ways through which we damage the soil are many. And the alarming decline is forecast to continue as demand for food and productive land increases while pressure from climate change, population growth, urban development, waste, pollution, and the need for more (and cheaper) food mounts.
According to WWF, half of the world’s topsoil has been lost in the past 150 years only. Barring any imminent and successful widespread adoption of hydro-culture (an up-to-now unattainable proposition that comes with its own environmental drawbacks), we simply cannot and will not grow food to feed 7.8 billion people, and counting, without soil.
To access more soil for agriculture, we cut down forests. However, as noted by WWF, “When agriculture fields replace natural vegetation, topsoil is exposed and can dry out. The diversity and quantity of microorganisms that help to keep the soil fertile can decrease, and nutrients may wash out. Soil can be blown away by the winds or washed away by rains.” And cutting down forests has, in any case, a litany of dangerous effects on our ecosystem.
It is evident; things need to change and fast. All farmers, growers and consumers should have a common goal to protect, maintain and build their most vital asset – soil.
What we find interesting:
→ The Soil Association, UK’s leading membership charity campaigning for healthy, humane and sustainable food, farming and land use.
What can be done to save our soils? We first need to think of them as alive: The soil matrix is a combination of organisms, minerals and organic matter, which interact with and impact one another.
“In fact, one teaspoon of healthy soil can contain as many as one billion bacteria, plus fungi, protozoa and nematodes”, explains FoodPrint. Soil is alive, and it is vulnerable, for it takes anything between 100 and 1,000 years to develop.
To protect our soils, and help them regenerate, we need to rethink what and how we eat. We need soil for agriculture, but it is agriculture that is killing our soil.
We also need to remember that we are connected to our soil: We eat what comes from it, so if it is bad for the soil, it is bad for us, and if it is good for the soil it is most probably good for us too.
“Let’s try and organically grow crops […] you don’t need to think about large scale farming as being pesticide-driven mechanical farming”, says Owen.
Following sustainable agriculture practices means limited to no synthetic pesticides use, relying on compost, green manure and mulching.
“Farmers are getting into what is called cover crops. They realise that instead of ploughing the land, you are better off planting a cover crop, and let that cover crop effectively replenish the soils”, Owen adds.
These practices not only improve the health of our soils, but they also lead to healthier produce, containing more and higher quality vitamins and minerals, therefore making us healthier.
Alternatively, we can let nature do what nature does best when left alone: “Let nature take it over for a while because it is amazing what happens,” says Owen.
There is an increasing realisation that soil life may be the key to crop productivity, but little research is being invested in this area, and substantial knowledge gaps remain. The Global Ecology Group dedicates time and resources analysing soils and soil organisms, an essential first step to support soil health.
After all, GEG’s research and development is inspired by nature. We apply this inspiration to human needs by respecting our interconnectedness and interdependence with nature, and by working sustainability for the future of our species and our planet.
As a critical response to the COVID-19 pandemic, GEG currently manufactures mobile and static decontamination systems delivering ECAS dry fog to efficiently sanitise critical infrastructure such as hospital wards, or emergency vehicles such as ambulances, and health care workers’ gear.
The ECAS technology at a glance
Electrochemically activated solutions (ECAS), or simply electrolysed water, manufactured by the Global Ecology Group (GEG), is a unique disinfectant with the germ-killing properties of chlorine but is non-toxic, and safe to humans, animals and the environment. ECAS contain hypochlorous acid – known more widely as HOCl. It is 100 times more effective as a disinfectant than bleach, killing germs and viruses instantly.
→ A unique non-toxic disinfectant with rapid germ-killing properties.
ECAS exterminates 99.95 percent of germs that it comes into contact with – it causes bacteria to literally burst by breaking their cell membrane apart. ECAS is also characterised by a rapid killing time demonstrated on Escherichia coli (E. col), SARS coronavirus (SARS-CoV), Norovirus, Avian influenza virus (AI), Swine influenza virus (SIV), human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV), Poliovirus, Legionella bacteria, Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus bacteria (MRSA) and Clostridioides difficile bacteria (C. diff).
→ It exterminates 99.9% of bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa.
In addition to the drinking water industry, ECAS and ECAS generators are commercially available in various other industrial sectors, delivered through either spraying or static and mobile decontamination fogging systems. The ECAS fogging systems are ideal to sanitise buildings and vehicles, while sprays are great for sanitising surfaces and hands. ECAS has been widely and safely used in the food industry.
→ Delivered through static and mobile fogging systems, or through spraying.
In a nutshell: The science behind and Efficacy of ECAS
ECAS – made from salt (NaCl), water (H2O) and electricity – works by oxidising pathogens and is non-toxic, rapidly degradable and has a broad-spectrum of antimicrobial activity. ECAS is produced via the electrolysis of a low mineral salt solution in an electrochemical cell. This results in a split: a positively-charged solution and a negatively-charged one. The negative solution contains a mix of relatively short-lived reactive oxidants that kill pathogens. After use, ECAS ultimately reverts to salt and water.
→ ECAS is made from salt (NaCl), water (H2O) and electricity.
Numerous studies have demonstrated the virucidal activity of electrolysed water against a broad range of targets. The broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity of electrolysed water enables high-level disinfection as defined by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and their favourable biocompatibility means that electrolysed water is ideally suited as both an environmental decontaminant and in the control or treatment of skin surface or mucous membrane infections. It is expected that surface disinfection with ECAS to significantly reduces coronavirus infectivity on surfaces within one minute exposure time and a similar effect against the COVID-19 (SARS-CoV-2).
→ Some examples of scientific evidence:
- 99.999% of the highly pathogenic Asian Avian Influenza A (H5N1) Virus and the low-pathogenic H9N2 virus were destroyed one minute after applying the electrolysed water >>> Read more
- Fogged electrolysed water has been found to significantly reduce the surface levels of both human Norovirus and surrogate viruses and has shown significant activity against human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). >>> Read More
- Electrolysed water can be regarded as a cost-effective disinfectant that is successful in controlling hospital infections, as it also has an effect on various bacteria with resistance capabilities. >>> Read more
- Electrolysed water has no systemic effects and is safe as a sanitiser. >>> Read more
Modern industry and living consume unbelievable amounts of our most precious resource water. Using water more efficiently demands a paradigm shift and an ethical revolution in addition to technical solutions.
Over the last century, water use has grown at more than twice the rate of population increase globally, and it is still increasing in all sectors. The effects of climate change will intensify the risk of droughts as well. While some regions are experiencing heavy floods, others are suffering from increasing aridity.
In both cases, the affected people face the same problems: a lack of clean drinking water and often lack water for agriculture. Poor access to water is not only a threat to people’s health but also livelihoods. It limits the potential to irrigate crops or undertake other water-dependent activities.
In some countries, water scarcity is so pronounced that humans cannot reach many of the desired economic, social, and environmental goals. Over 2 billion people live in countries experiencing high water stress today and the numbers will continue to increase. The need for greater access to reliable and clean water has therefore risen to the top of the development agenda of many countries in recent years.
In contrast, in Europe, the average person directly consumes between 100-150 litres of water a day – like drinking water, for washing clothes, bathing and watering plants. But each person also indirectly consumes anywhere between 1,500 and 10,000 litres of water per day, depending on where they live and their consumption habits.
-> Save Water: Reduce Your Water Footprint
If business as usual continues, the global demand for water will exceed viable resources by 40 percent by 2030. Therefore, using the critical elements water more efficiently is a top priority. “Water is something that we should all be focusing on. As a resource, we should really make sure we keep it, as much as we can,” says the Global Ecology Group (GEG) Founder and CEO Owen J. Morgan.
The global water crisis has many causes, requiring many different solutions. These solutions must span policy, behaviour change and innovative technology, such as water conservation and recycling technologies, to make a real difference.
Industrial water use accounts for approximately 22 percent of global consumption. The corporate footprint includes water that is directly and indirectly consumed when goods are produced. Much of this cannot be returned into the natural cycle or used for consumption leaving a huge untapped resource of water remain unfit for purpose.
However, GEG’s Founder and CEO Owen J. Morgan has already proven restoration of water from some of the most polluted sources, for example, mine water, drilling discharge and medical waste.
“We don’t need to go down the road of putting huge amounts of chemicals into the water to make it better. We can fix water by actually looking at what nature does,” says Owen.
Since the early 1990s, Owen has been developing a number of water recovery processes. These key technologies follow specific approaches to recovery of contaminated water to a natural balanced and in many cases a potable water supply.
GEG’s research and development is inspired by nature. We apply this inspiration to human needs by respecting our interconnectedness and interdependence with nature, and by working sustainability for the future of our species and our planet.
As a species, we have looked towards nature as a source of inspiration for our human aspirations. However, mass replicating nature’s solutions without causing harm remains challenging.
He was sitting in his mother’s garden at Woolsthorpe Manor in Lincolnshire, probably contemplating some profound philosophical idea, when while vaguely gazing at the horizon, he saw an apple fall from his mother’s apple tree. This prompted him to ask: “Why sh[oul]d that apple always descend perpendicularly to the ground […].” This is the myth around Sir Isaac Newton’s first contemplations of his law of universal gravitation. This is also one example of how nature can inspire us, lead us and teach us about ourselves, our surroundings and our potentials.
When we look at the scientific advances we have achieved as a species, it is easy to discount the role nature played and continues to play in pushing forward these developments.
We have built our planes by first observing birds, manufactured our submarines by learning from whales and tuned our sonars by listening in to bats and dolphins. This is what is generally referred to as biomimicry, the practise of looking deeply into nature for solutions to engineering, design and other challenges. We simply try to figure out where our challenge can be found in nature, and what strategy or pattern nature developed to overcome or transcend it. This process of observation is the first step to learn from nature truly.
The second step is to creatively scale up nature’s solutions to fit our human frameworks. While working on this, we must be aware of the challenges this scaling and fitting processes may present. Generally, it is not difficult to transpose nature’s solutions to fit our needs. What is challenging is to achieve this without violating nature’s laws of interconnectedness, interdependence and sustainability.
The story of morphine, for example, has gone through the steps described above. The pain-relieving qualities of opium have been known and exploited for centuries. These qualities had always been extracted from the natural plant itself. In our modern age, however, “the pharmaceutical industry believed nature could not provide enough of the actual raw materials, to grow enough poppies to feed an opiate market. Much easier [they thought] is to synthesise the molecular structure”, explains the Founder and Chief Executive Officer of the Global Ecology Group, Owen J. Morgan.
Synthesised morphine was the result of the pharmaceutical industry’s attempts to take something that nature provides and fit it into a human framework of consumption. However, as explained by Brook, Bennet and Desai in their paper entitled ‘The Chemical History of Morphine: An 8000-year Journey, from Resin to de-novo Synthesis’, “our attempts to synthesise morphine, despite our advanced knowledge in synthetic chemistry, are still no match for the plant-based extraction of morphine from the poppy plant”. As we are part of nature, “if we put a synthetic into our body, it doesn’t matter how close we have replicated nature, we have missed parts of those building blocks, because we don’t understand all those building blocks”, explains Owen.
Nature is filled with examples that can benefit us, from healing plants to creative, cooperative networks. The mass scaling of nature’s solutions has always been the problematic sequence in our attempts to learn from nature.
How do we bridge this gap? Only by always respecting nature’s laws of interconnectedness, interdependence and sustainability. If our mass scaling claims to be “independent” from nature, this is a first sign that we are off track. If we do not consider the impact of our innovations on us, our environment, other species and the future, it is then a sure sign that we need to reconsider our steps. In the words of Owen, “nature can provide us with all these life-giving and healing properties, why don’t we figure out how to work with nature to actually have a beneficial relationship, so that we coexist?”
GEG seeks to do precisely that. Our research and development, as well as our innovations, such as Ennea and the Harvester, are inspired by nature. We apply this inspiration to human needs by respecting our interconnectedness and interdependence with nature, and by working sustainability for the future of our species and our planet.
We are, as a human species, facing a critical crossroad. Our actions will dictate whether our descendants will live a life of deprivation or abundance.
This resonates with many in the younger generations. These same thoughts echoed in Greta Thunberg’s words when she declared that “we are facing a mass extinction”, denouncing her audience at the United Nations Climate Action Summit in New York for stealing her dreams and her childhood, to the applause of that same assembly.
What Greta and other individuals and organisations, such as Extinction Rebellion are referring to when they level this criticism, is something inherent to any positive change: Responsibility.
Responsibility, in the sense of being accountable, is greatly lacking in our politics, our policies and our businesses. The concept of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) was coined as a way to signify Big Business’ steps towards acknowledging this responsibility. CSR is at best, however, a superficial remedy dealing with symptoms only. Responsibility cannot mean diverging some of our income to “do good”, it means to be accountable throughout all aspects, processes, goals and achievements of our businesses. This, in turn, requires a shift in vision.
Popular wisdom dictates that business’ only creed is profit. Consequently, using all measures necessary to achieve this goal is a given and a right. Nature is also a means to that end. Talking about care for nature as a necessary and integral part of a business model was for a long time a laughable proposition. Up to now, many businesses view this as a matter of secondary concern, while for others, it is a direct threat to their profit-making principle.
A shift in vision means a fundamental change in our business philosophy. Such a change, however, takes time – time that we cannot afford. So how do we start, as businesses, to ‘be responsible’? We need to ‘feel responsible’. This feeling of responsibility starts, as the Founder and Chief Executive Officer of the Global Ecology Group, Owen J. Morgan describes, by viewing ourselves as “caretakers of life itself”. It is only when we hold this view that everything else falls into place: Care for nature and profit-making are no longer mutually exclusive realities.
At the Global Ecology Group, we act as a catalyst for this vision change, by providing working systems and solutions to different industries and sectors, enabling them to make real steps towards ‘being responsible’.
Through innovations like Ennea and the Harvester, GEG’s Research and Development paves the way towards establishing industry practices which bring together the two sides of the responsible-business equation – both reaching business goals and meeting complex environmental challenges. This is our way to build a legacy of symbiosis, where human growth connotes care for life itself.

Last updated April 30, 2020
Thank you for choosing to be part of our community at Global Ecology Group Ltd (GEG) (“Company”, “we”, “us”, or “our”). We are committed to protecting your personal information and your right to privacy. If you have any questions or concerns about our notice or our practices concerning your personal information, please contact us at: hi[at]globalecology.group
When you visit our website https://globalecology.group and use our services, you trust us with your personal information. We take your privacy very seriously. In this privacy notice, we describe our privacy notice. We seek to explain to you in the most precise way possible what information we collect, how we use it, and what rights you have concerning it. We hope you take some time to read through it carefully, as it is important. If there are any terms in this privacy notice that you do not agree with, please discontinue use of our Sites and our services.
This privacy notice applies to all information collected through our website (such as https://globalecology.group), and/or any related services, sales, marketing or events (we refer to them collectively in this privacy notice as the “Services”).
Please read this privacy notice carefully as it will help you make informed decisions about sharing your personal information with us.
TABLE OF CONTENTS
1. WHAT INFORMATION DO WE COLLECT?
2. WILL YOUR INFORMATION BE SHARED WITH ANYONE?
3. DO WE USE COOKIES AND OTHER TRACKING TECHNOLOGIES?
4. HOW LONG DO WE KEEP YOUR INFORMATION?
5. HOW DO WE KEEP YOUR INFORMATION SAFE?
6. WHAT ARE YOUR PRIVACY RIGHTS?
7. CONTROLS FOR DO-NOT-TRACK FEATURES
8. DO WE MAKE UPDATES TO THIS POLICY?
9. HOW CAN YOU CONTACT US ABOUT THIS POLICY?
1. WHAT INFORMATION DO WE COLLECT?
Information automatically collected
In Short: Some information – such as IP address and/or browser and device characteristics – is collected automatically when you visit our Services.
We automatically collect certain information when you visit, use or navigate the Services. This information does not reveal your specific identity (like your name or contact information) but may include device and usage information, such as your IP address, browser and device characteristics, operating system, language preferences, referring URLs, device name, country, location, information about how and when you use our Services and other technical information. This information is primarily needed to maintain the security and operation of our Services, and for our internal analytics and reporting purposes.
Like many businesses, we also collect information through cookies and similar technologies.
2. WILL YOUR INFORMATION BE SHARED WITH ANYONE?
In Short: We only share information with your consent, to comply with laws, to provide you with services, to protect your rights, or to fulfil business obligations.
We may process or share data based on the following legal basis:
-> Consent: We may process your data if you have given us specific consent to use your personal information within a particular purpose.
-> Legitimate Interests: We may process your data when it is reasonably necessary to achieve our legitimate business interests.
-> Performance of a Contract: Where we have entered into a contract with you, we may process your personal information to fulfil the terms of our contract.
-> Legal Obligations: We may disclose your information where we are legally required to do so in order to comply with applicable law, governmental requests, a judicial proceeding, court order, or legal process, such as in response to a court order or a subpoena (including in response to public authorities to meet national security or law enforcement requirements).
-> Vital Interests: We may disclose your information where we believe it is necessary to investigate, prevent, or take action regarding potential violations of our policies, suspected fraud, situations involving potential threats to the safety of any person and illegal activities, or as evidence in litigation in which we are involved.
More specifically, we may need to process your data or share your personal information in the following situations:
-> Vendors, Consultants and Other Third-Party Service Providers. We may share your data with third-party vendors, service providers, contractors or agents who perform services for us or on our behalf and require access to such information to do that work. Examples include: payment processing, data analysis, email delivery, hosting services, customer service and marketing efforts. We may allow selected third parties to use tracking technology on the Services, which will enable them to collect data about how you interact with the Services over time. This information may be used to, among other things, analyse and track data, determine the popularity of certain content and better understand online activity. Unless described in this Policy, we do not share, sell, rent or trade any of your information with third parties for their promotional purposes.
-> Business Transfers. We may share or transfer your information in connection with, or during negotiations of, any merger, sale of company assets, financing, or acquisition of all or a portion of our business to another company.
-> Third-Party Advertisers. We may use third-party advertising companies to serve ads when you visit the Services. These companies may use information about your visits to our website (s) and other websites that are contained in web cookies and other tracking technologies to provide advertisements about goods and services of interest to you.
3. DO WE USE COOKIES AND OTHER TRACKING TECHNOLOGIES?
In Short: We may use cookies and other tracking technologies to collect and store your information.
We may use cookies and similar tracking technologies (like web beacons and pixels) to access or store information. Specific information about how we use such technologies and how you can refuse certain cookies is set out in our Cookie Policy.
4. HOW LONG DO WE KEEP YOUR INFORMATION?
In Short: We keep your information for as long as necessary to fulfil the purposes outlined in this privacy notice unless otherwise required by law.
We will only keep your personal information for as long as it is necessary for the purposes set out in this privacy notice unless a more extended retention period is required or permitted by law (such as tax, accounting or other legal requirements). No purpose in this policy will require us keeping your personal information for longer than two (2) years.
When we have no ongoing legitimate business need to process your personal information, we will either delete or anonymise it, or, if this is not possible (for example, because your data has been stored in backup archives), then we will securely store your personal information and isolate it from any further processing until deletion is possible.
5. HOW DO WE KEEP YOUR INFORMATION SAFE?
In Short: We aim to protect your personal information through a system of organisational and technical security measures.
We have implemented appropriate technical and organisational security measures designed to protect the security of any personal information we process. However, please also remember that we cannot guarantee that the internet itself is 100% secure. Although we will do our best to protect your personal information, the transmission of personal information to and from our Services is at your own risk. You should only access the services within a secure environment.
6. WHAT ARE YOUR PRIVACY RIGHTS?
In Short: In some regions, such as the European Economic Area, you have rights that allow you greater access to and control over your personal information. You may review, change, or terminate your account at any time.
In some regions (like the European Economic Area), you have certain rights under applicable data protection laws. These may include the right (i) to request access and obtain a copy of your personal information, (ii) to request rectification or erasure; (iii) to restrict the processing of your personal information; and (iv) if applicable, to data portability. In certain circumstances, you may also have the right to object to the processing of your personal information. To make such a request, please use the contact details provided below. We will consider and act upon any request following applicable data protection laws.
If we are relying on your consent to process your personal information, you have the right to withdraw your consent at any time. Please note, however, that this will not affect the lawfulness of the processing before its withdrawal.
If you are resident in the European Economic Area, and you believe we are unlawfully processing your personal information, you also have the right to complain to your local data protection supervisory authority. You can find their contact details here: http://ec.europa.eu/justice/data-protection/bodies/authorities/index_en.htm
Cookies and similar technologies: Most Web browsers are set to accept cookies by default. If you prefer, you can usually choose to set your browser to remove cookies and to reject cookies. If you wish to remove cookies or reject cookies, this could affect certain features or services of our Services. To opt-out of interest-based advertising by advertisers on our Services visit http://www.aboutads.info/choices/.
7. CONTROLS FOR DO-NOT-TRACK FEATURES
Most web browsers and some mobile operating systems and mobile applications include a Do-Not-Track (“DNT”) feature or setting you can activate to signal your privacy preference not to have data about your online browsing activities monitored and collected. No uniform technology standard for recognising and implementing DNT signals has been finalised. As such, we do not currently respond to DNT browser signals or any other mechanism that automatically communicates your choice not to be tracked online. If a standard for online tracking is adopted that we must follow in the future, we will inform you about that practise in a revised version of this privacy notice.
8. DO WE MAKE UPDATES TO THIS POLICY?
In Short: Yes, we will update this policy as necessary to stay compliant with relevant laws.
We may update this privacy notice from time to time. The updated version will be indicated by an updated “Revised” date, and the updated version will be effective as soon as it is accessible. If we make material changes to this privacy notice, we may notify you either by prominently posting a notice of such changes or by directly sending you a notification. We encourage you to review this privacy notice frequently to be informed of how we are protecting your information.
9. HOW CAN YOU CONTACT US ABOUT THIS POLICY?
If you have questions or comments about this policy, you may email us at hi[at]globalecology.group or by post to:
Global Ecology Group Ltd (GEG)
The Old Police Station
Whitburn Street,
Bridgnorth V16 4QP
United Kingdom
How can you review, update, or delete the data we collect from you?
Based on the laws of some countries, you may have the right to request access to the personal information we collect from you, change that information, or delete it in some circumstances. To request to review, update, or delete your personal information, please submit a request to hi[at]globalecology.group. We will respond to your request within 30 days.
About
We are meeting unprecedented challenges, which mostly stream from our unwillingness to take nature as an equal partner in our endeavours. For most industries, this means acting, by choice or default, from the misled understanding that care for the environment and profit-making are mutually exclusive realities.
The Global Ecology Group (GEG) sets a different trend. We look at challenges or problems and figure out solutions and workarounds derived from nature, translating her wisdom, ensuring both harmony and usefulness.
Our ethos is respecting the sanctity of the natural world and our place in it. We, therefore, work towards upholding ecological integrity in all aspects of our work and building a balanced global ecology.
The protection and care for our planet must come first, but this does not mean that profitability needs to come in second. Through innovations like Ennea and the Harvester, GEG’s Research and Development paves the way towards improving current industry practices by meeting complex environmental challenges.
With purpose and agility, GEG combines science, technology and inspiration to bring forth progressive approaches supporting our government, non-governmental and commercial partners to reach their goals.
We help our partners by providing benign eco-technology with a minimal environmental impact and contribute to healing our planet by reducing and remediating hazardous waste and toxic byproducts created by industry, conflict and natural disasters.
Responsible profit is no longer an alternative – it is a necessity, for us and our planet. GEG supports your business to fulfil it. Get in touch with us!
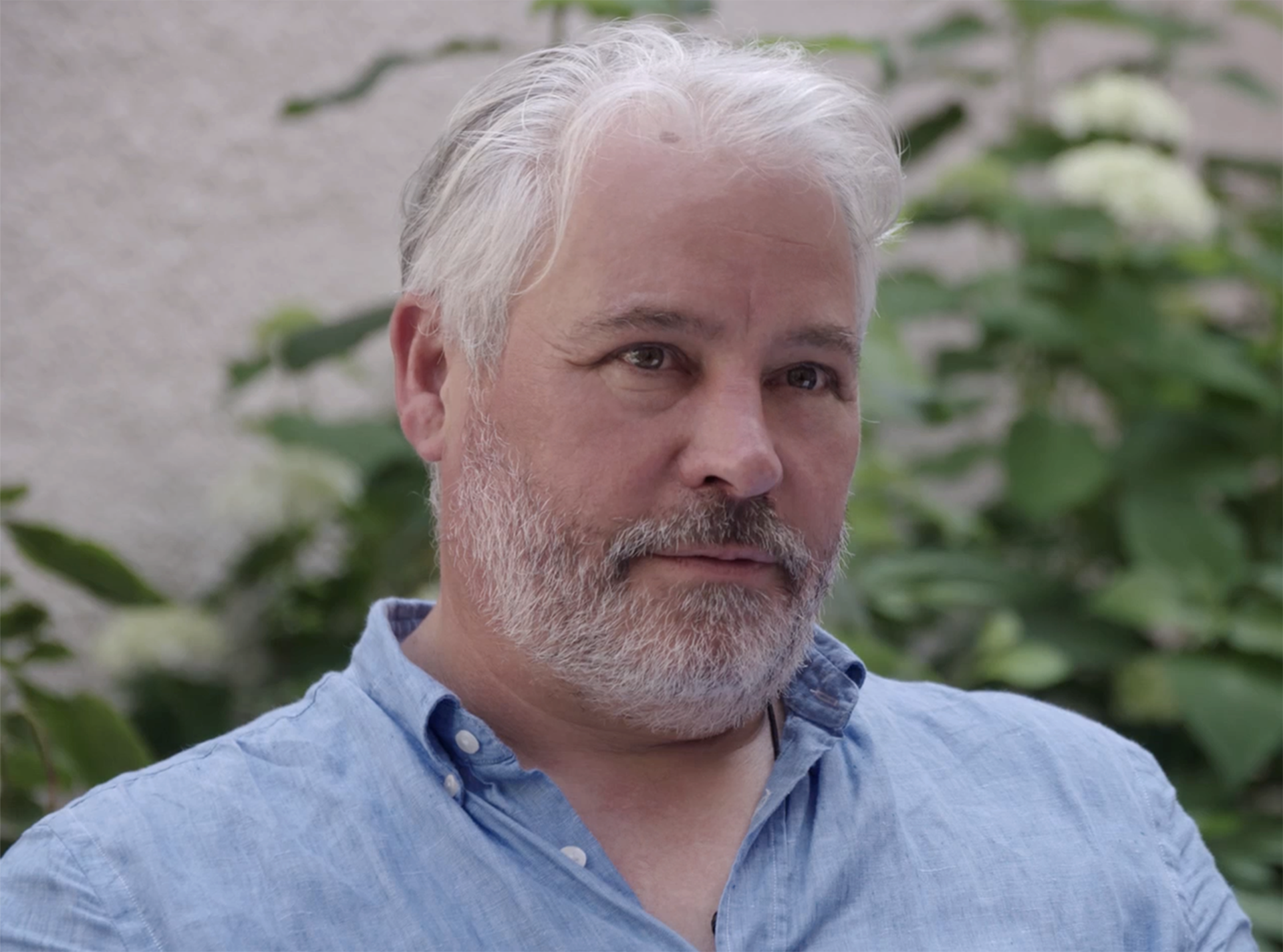

Owen J. Morgan is a caring genius. His life journey has taken him to unusual places, where he lived through amazing and challenging experiences. In Europe, the Americas and Africa, he learned, achieved, and inspired. Founding GEG is Owen’s current chosen path to care for planet Earth and the abundant life on it. He infuses the company with his worldview, gathering like-minded people in a group bound by care and responsibility to ensure better outcomes for projects, people and the environment.
Owen has a long list of innovations and achievements to his name, including Ennea and the Harvester.
He started with producing digital archival fine art print, creating the first one in the world in 1991.
Since 1994, Owen has been fully committed to researching and developing a wide range of eco-technologies – alternative environmentally friendly solutions for the rehabilitation and secondary recovery of industrial waste, groundwater pollution and heavy oil soil remediation. His know-how has been instrumental in meeting real-world disasters with ethically responsible countermeasures.
Owen has also spent considerable time in Ethiopia, devising strategies and actionable data on how to improve the mining sector, for example, ensuring miners safety and environmental protection.
If you start a conversation with Owen, you can be sure he will inspire you with his far-sighted thinking, perseverance and passion for learning from nature and translating her wisdom into practical solutions.
It is precisely this inspiration provided by Owen that enables GEG to contribute to a more balanced, holistically fair and healthy future, for us and our planet.
Projects
At the heart of the Global Ecology Group is the quest for discovery and learning, derived from and inspired by the five elements of nature: Earth, Air, Fire, Water and Aether.
The five elements guide GEG’s Research and Development in its pursuit to understand the laws of nature and to attain greater health and balance for all living beings – be it human beings, plants, animals, or any other living organism.
Essentially, the interplay of the five elements forms the universal and interconnected cycle of life that not only inspires GEG’s solutions but also provides the normative framework for the company’s approach and decisions.
At the Hive, GEG’s UK Research and Development facility, we have the unique ability to go from theory, laboratory trials to commercial-scale projects sometimes in months.
These in-house capabilities in the research, development and deployment of breakthrough approaches and eco-technologies provide our partners with the best possible solutions to the problems and challenges they face.
Additionally, GEG’s full-service laboratory offers a complete range of provisions, for example, the analysis and optimisation of a variety of substances and formulations, or the extraction of bioactive compounds from organic material.
We thrive on fixing your problems, nature’s way, for us and our planet.
GEG’s Ennea Process is a gentle revolution in biogenic extraction. It is the answer to what both nature and the market demand: higher yields with higher quality, less waste with less environmental impact.
The existing methods of extracting bioactive compounds and essential oils, such as steam distillation, conventional solvent and supercritical carbon dioxide extraction suffer from many operational disadvantages and environmental drawbacks.
Ennea is an economical and practical solution to all problems associated with conventional extraction processes. This new process is elegant in concept yet simple and safe in operation.
The Ennea Processor is a radical departure from the methods in use today. Through Ennea, bioactive compounds are acquired, individually and as a whole, from fresh and dry biomass – from flowers and leaves to stems and roots.
Ennea transcends the current limits of the industry, encouraging a market of quality and affordability, to the benefit of both enterprises and people. Ennea is the healthier choice, for us and our planet.
Oxygen and water are fundamental components of nature. Their balance creates vitality and improves the quality of life. Optimal oxygen uptake is essential to maintain people, animals, and plants’ bio reactions.
Unfortunately, environmental degradation and pollution compromise this balance.
Supplementary oxygen is needed to upkeep this fragile balance, and water is an effective vehicle for transporting oxygen to all cells, fuelling metabolism.
Therefore, GEG developed the OKHIO restructured water solutions, creating oxygen enriched active water.
Water restructured with the GEG OKHIO technology comes with many benefits that help people, animals and plants to stay active and healthy.
GEG’s OKHIO systems can be used in a wide range of applications, providing oxygen enriched active water unique in its purity.
GEG’s Harvester is a breakthrough eco-technology developed for the mining sector to harvest minerals and precious metals. It is the answer to what both nature and the market demand.
Using neither water nor chemicals and with low energy requirements, the Harvester has a minimal environmental impact. Yet, the system delivers near-total resource harvesting, with a 99% recovery of precious metals and stones, such as alluvial gold and diamonds.
The Harvester requires minimal infrastructure and is highly scalable. The system may be deployed as a small-scale portable unit to be used in the field or as a large-scale installed commercial unit.
Elegant in concept yet safe and straightforward in operation, the Harvester offers both, small scale artisanal miners and large scale mining endeavours, a way out of the many drawbacks of conventional mining.
The Harvester is the equitable and profitable necessity transforming the mining sector, for us and our planet.
Killing germs is killing our planet, but it doesn’t have to be this way. Electrochemically activated solutions (ECAS) are unique and accessible sanitisation solutions, which not only protect from microbes, but also respect the need for a safe application, both for people and nature.
The existing methods of sanitisation often pose significant threats to our health and harm the environment. ECAS are safe and sustainable alternatives, for example, to disinfect buildings, control biofilm, disinfect drinking water, preserve fruits and vegetables, or prevent legionella. ECAS are efficient, non-toxic and biodegradable.
The broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity of ECAS enables high-level disinfection as defined by the Center for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), and the favourable biocompatibility means ECAS are ideally suited as both environmental decontaminants and in the control or treatment of skin surface or mucous membrane infections.
To manufacture ECAS only water, salt and electricity are needed. ECAS are economical and practical solutions which guarantee fast microbe kill time, and thorough protection through various deployment techniques such as fogging systems to sanitise entire buildings or vehicles, and sprays to sanitise surfaces and hands.
ECAS are already successfully used across the globe, for example, to protect our food from microbes, making it safer to consume. ECAS can be used everywhere, including homes, hospitals, ambulances and stores. ECAS can also be used to sanitise equipment and gear used by health care workers and caregivers.
The Global Ecology Group (GEG) therefore develops and advances ECAS deployment solutions – a necessity that protects us, our loved ones and our environment.